Calculate nodal distance to skin
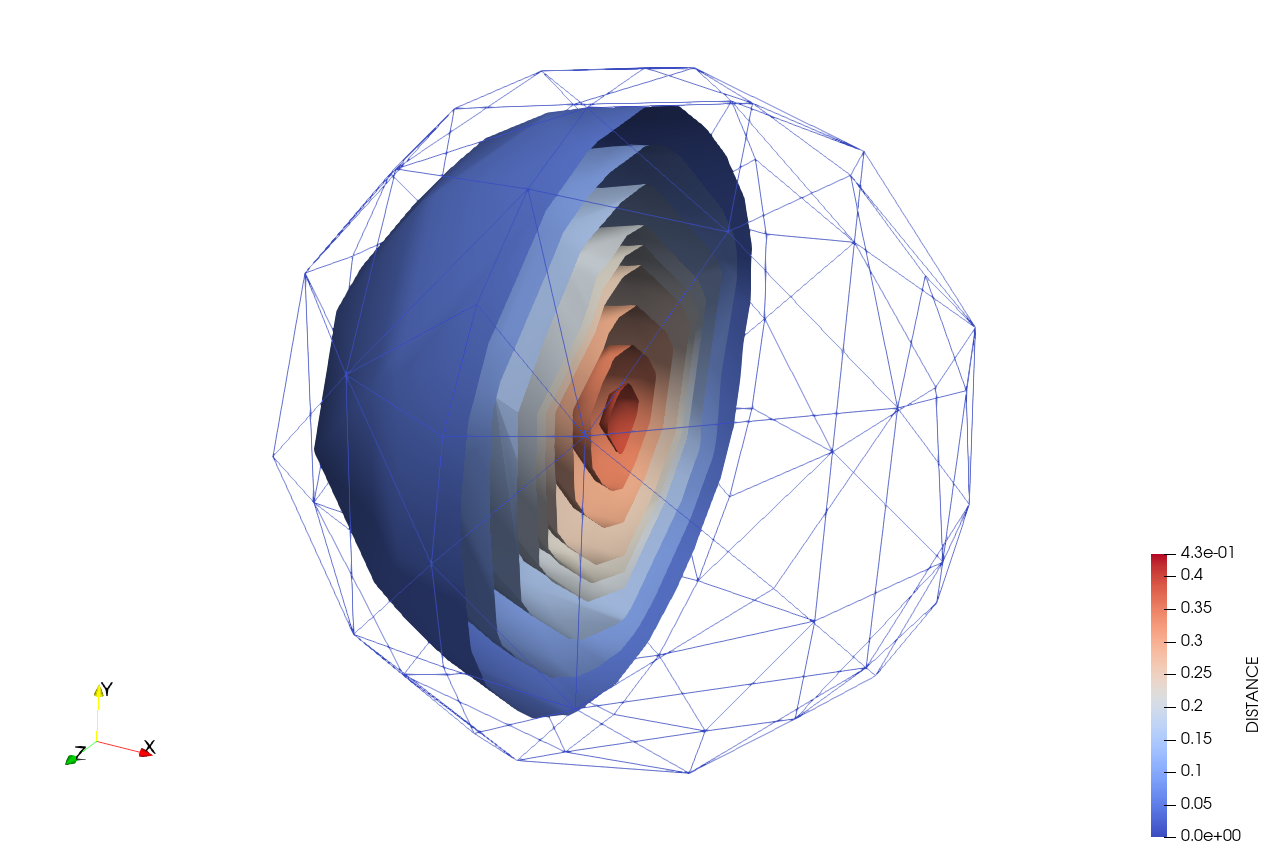
Description
This process offers a robust solution for calculating the minimum distance from the nodes of a volume model part to a designated skin model part using the GeometricalObjectBins in order to compute the distance.
Key Features
-
Mesh Compatibility: This ensures that it works with any type of mesh, current processes are focused in simplex meshes and usually compute signed distance (this distance is not signed) and it is more focus on the cut of elements.
-
Unsigned Distance Calculation: Distance is unsigned and exclusively and solely calculated within the nodes.
-
Support for Historical and Non-Historical Data: This process supports both historical and non-historical distance variables.
-
Support for Distance Calculation in the Skin if required: If required the maximum distance to a destination skin entity can be saved.
Future Developments
The process is currently optimized for serial execution. However, plans are underway to enable distributed computation, contingent on the integration of improvements from KratosMultiphysics/Kratos pull request #11719.
Execution
Execute
Execute method is used to execute the Process algorithms.
This algorithm defines 4 lambda functions for calculating the distance of nodes to the nearest geometrical object (element or condition) in a model part. It then determines which lambda to use based on whether the distance variable is historical or non-historical, and if we want to save the maximum distance to the found entity in the skin. Then it applies the appropriate lambda to calculate the distances.
-
distance_lambda_historical: This lambda function is used when working with historical data. It iterates over all nodes in the provided nods container and calculates the distance of each node to its nearest geometrical object using a spatial search. The calculated distance is then stored in the node’s historical data. -
distance_lambda_non_historical: This lambda function is similar todistance_lambda_historicalbut is used for non-historical data. It also calculates the distance of each node to its nearest geometrical object and stores the result in the node’s non-historical data container. -
distance_lambda_historical_save_skin: In addition to calculating distances using historical variables, this lambda also updates the skin model part with the calculated distance if the new distance is greater than the existing value. -
distance_lambda_non_historica_save_skin: Performs the same operations asdistance_lambda_historical_save_skinbut for non-historical variables.
These lambdas functions will be chosen depending on the flags mHistoricalValue and mSaveDistanceInSkin, one of the four lambda functions is selected for execution. This decision dictates whether historical or non-historical variables are used and whether distances are saved in the skin model part.
If the mSaveDistanceInSkin flag is set, initializes the distance variable to zero for all elements or conditions in the skin model part.
Both lambda functions take the following parameters:
Nodes: A reference to the container holding the nodes for which distances will be calculated.Bins: A reference to an object of typeGeometricalObjectsBins, which is used to perform efficient spatial searches for the nearest geometrical object to a given node.
The core of the distance calculation is performed by the Bins.SearchNearest(Node) call within each lambda. This function searches for the nearest geometrical object to the node and returns a search result object, from which the distance (GetDistance()) to the nearest object is retrieved and assigned to the node.
The selected lambda function is then applied to calculate the distances for all nodes in volumetric model part based on the geometrical objects (elements or conditions) found in skin model part. Before applying the lambda, the code checks whether to use elements or conditions from skin model part for the distance calculation, prioritizing elements if both exist.
⚠️ Warning
A warning is issued if both elements and conditions are found in the skin model part, indicating that elements will be considered for the distance calculation.
Flags
mHistoricalValue: Determines whether historical or non-historical variables are used for distance calculations.mSaveDistanceInSkin: Indicates whether the calculated distances should be saved back to the skin model part, updating the values if the new distance is greater than the existing one.
Parameters & Defaults
{
"volume_model_part" : "",
"skin_model_part" : "",
"distance_database" : "nodal_historical",
"save_max_distance_in_skin" : false,
"distance_variable" : "DISTANCE",
"skin_distance_variable" : "DISTANCE",
"visited_skin_flag" : "VISITED"
}
volume_model_part
Specifies the volume model part for the process. Absence of a value results in failure due to the default empty string.
skin_model_part
Defines the skin model part for distance computations. Like the volume model part, a default empty string necessitates explicit specification.
distance_database
This flag indicating whether historical variable is enabled or otherwise non-historical is considered. It is set by string, options are nodal_historical or nodal_non_historical. Default value is nodal_historical.
save_max_distance_in_skin
This flag indicates if the distance is going to be saved in the skin. By default is false, if activated will save the maximum distance in the found skin geometry and set the flag VISITED. This also deactivate shared memory parallelization.
distance_variable
Denotes the variable for applying the process, with DISTANCE set as the default value.
skin_distance_variable
Denotes the variable saved into the skin if save_max_distance_in_skin is active, with DISTANCE set as the default value.
visited_skin_flag
Denotes the flag to set when saving a value into the skin. Default is VISITED.